Hello cod3r’s i have prepared an example of Custom_Button with the help of .xml file’s
To help you understand shape drawable
What is shape drawable*
Shape drawable is nothing more just a collection of .xml file’s with that
you can create your own awesome Custom_Button as well as you can
create more with that.
Let’s Get Into Code!
Tutorial Level
Subscribe us for more tutorial’s LIKE THIS..
first of all after gradle sync
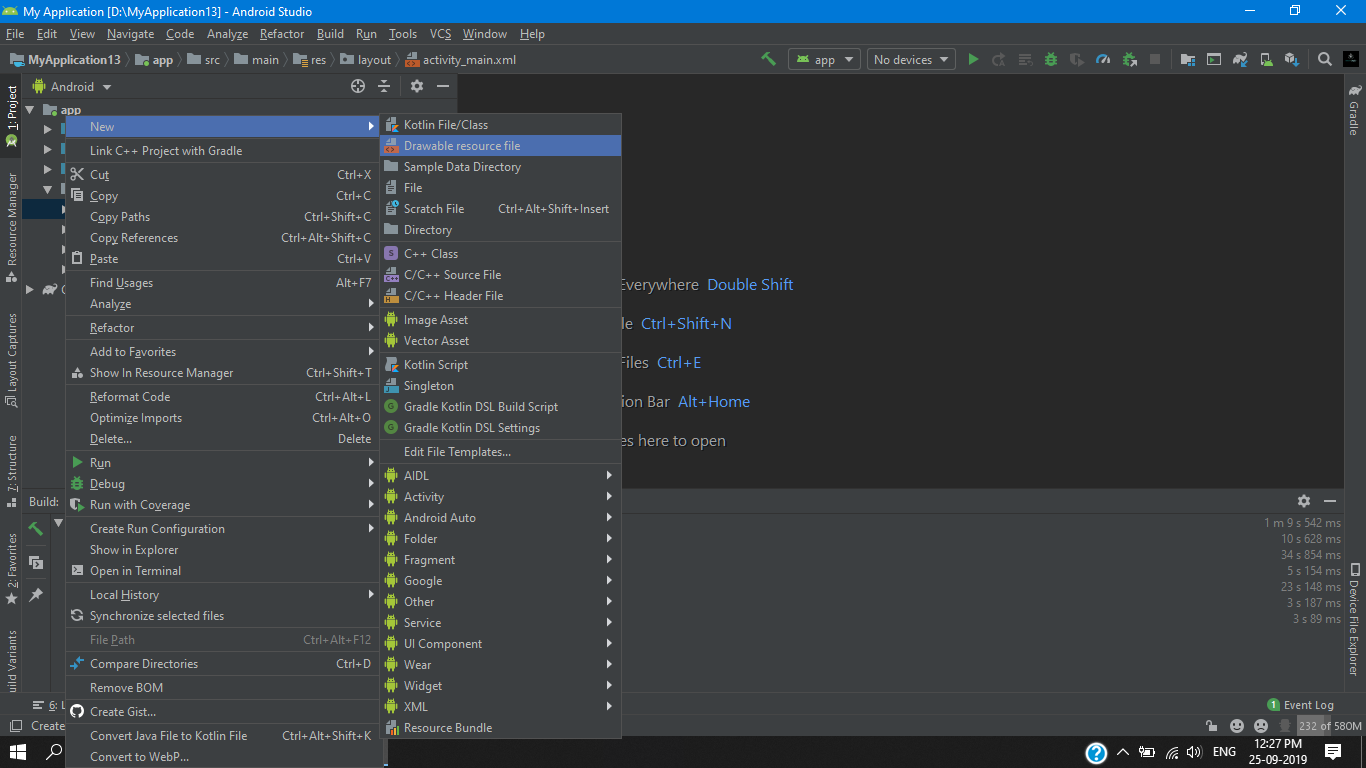
we need to create a new resource file so for that we will go intro res > drawable then we will right click on the drawable folder and pick a new resources file from the new section the first option on the popup menu. as you can see below.
we will name this file as our button_default then we hit ok after that we will have our first button_default.xml file so for this example we’ill need three .xml file’s but as for now we will work on this .xml file i will tell you more as we go further in this tutorial.
button_default.xml
first we change the default attribute to shape and give it another attribute android:shape=”rectangle”> and then we add another attribute <gradient in this we give end color and start color
android:startColor="#0000ff"
android:endColor="#fff"
for our gradient effect then we give some padding and a stroke,Corner’s as you can see below
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle"
>
<gradient
android:startColor="#0000ff"
android:endColor="#fff"
/>
<padding
android:bottom="7dp"
android:top="7dp"
android:right="7dp"
android:left="7dp"/>
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#9C27B0"/>
<corners android:radius="15dp"/>
</shape>

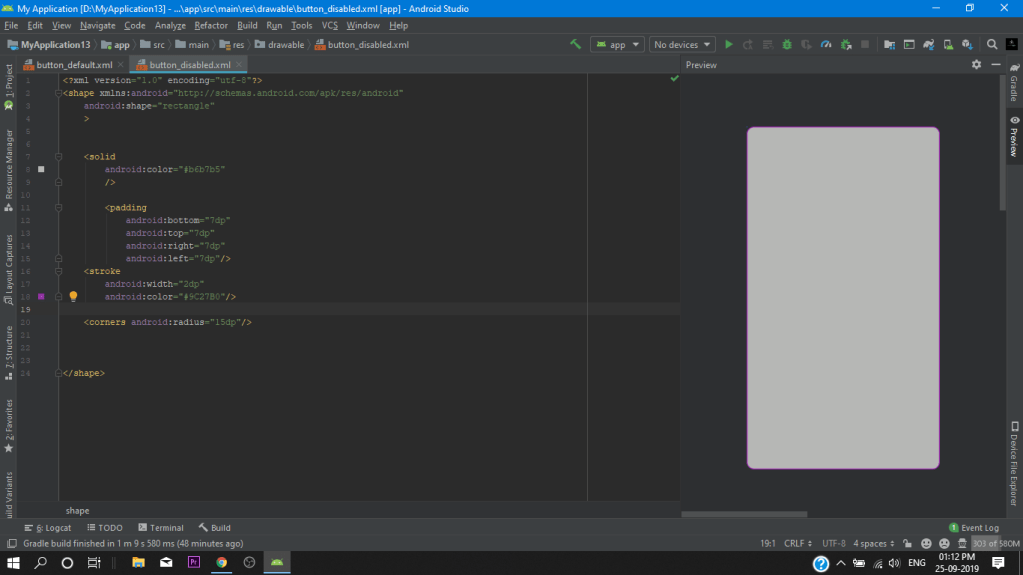
after completing our default_button.xml we copy all the codes for our two other .Xml file’s as i mentioned above so we go to our drawable folder again and create another resource file as button_disabled and we paste our code in it. then simply we change our color’s to gray as you can see below (for creating a disabled effect).
button_disabled.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle"
>
<solid
android:color="#b6b7b5"
/>
<padding
android:bottom="7dp"
android:top="7dp"
android:right="7dp"
android:left="7dp"/>
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#9C27B0"/>
<corners android:radius="15dp"/>
</shape>
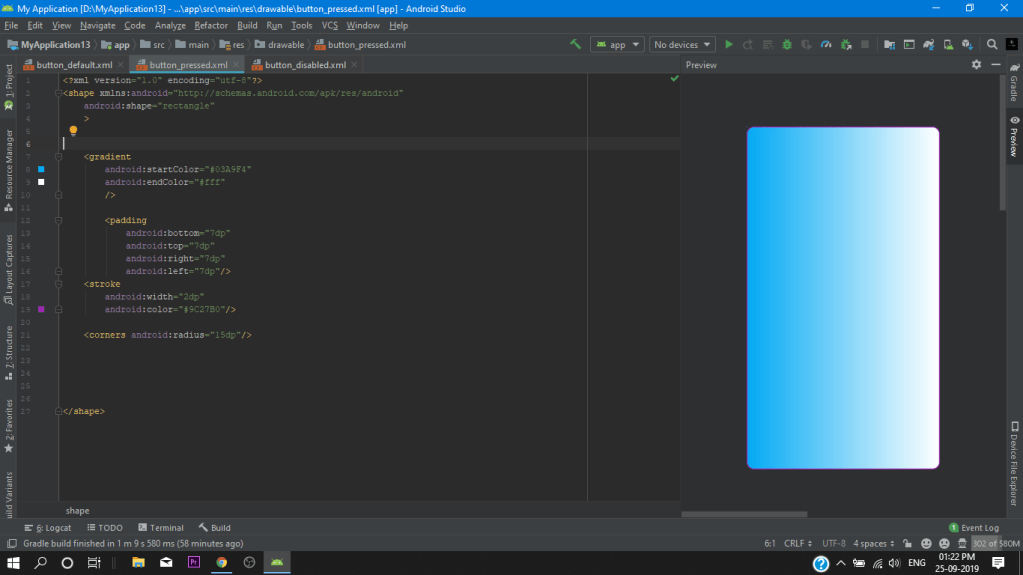
After that we create our 3rd resource file button_pressed.xml and again pase all code as we did earlier in the button_disabled.xml and just change the gradient color for a
(pressed effect).
android:startColor="#03A9F4"
android:endColor="#fff"
button_pressed.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shape="rectangle"
>
<gradient
android:startColor="#03A9F4"
android:endColor="#fff"
/>
<padding
android:bottom="7dp"
android:top="7dp"
android:right="7dp"
android:left="7dp"/>
<stroke
android:width="2dp"
android:color="#9C27B0"/>
<corners android:radius="15dp"/>
</shape>
We have successfully created our all resources file for our shape drawable and now we have to attached all the resources file to a single .xml file for we can call it in our project
we give it a name custom_button
custom_button.xml
in this xml we dont change the default attribute and in the selector we assign our button as you can see below
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item
android:state_pressed="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/button_pressed"/>
<item
android:state_enabled="false"
android:drawable="@drawable/button_disabled"/>
<item
android:drawable="@drawable/button_default"/>
</selector>
Main Activity.Xml
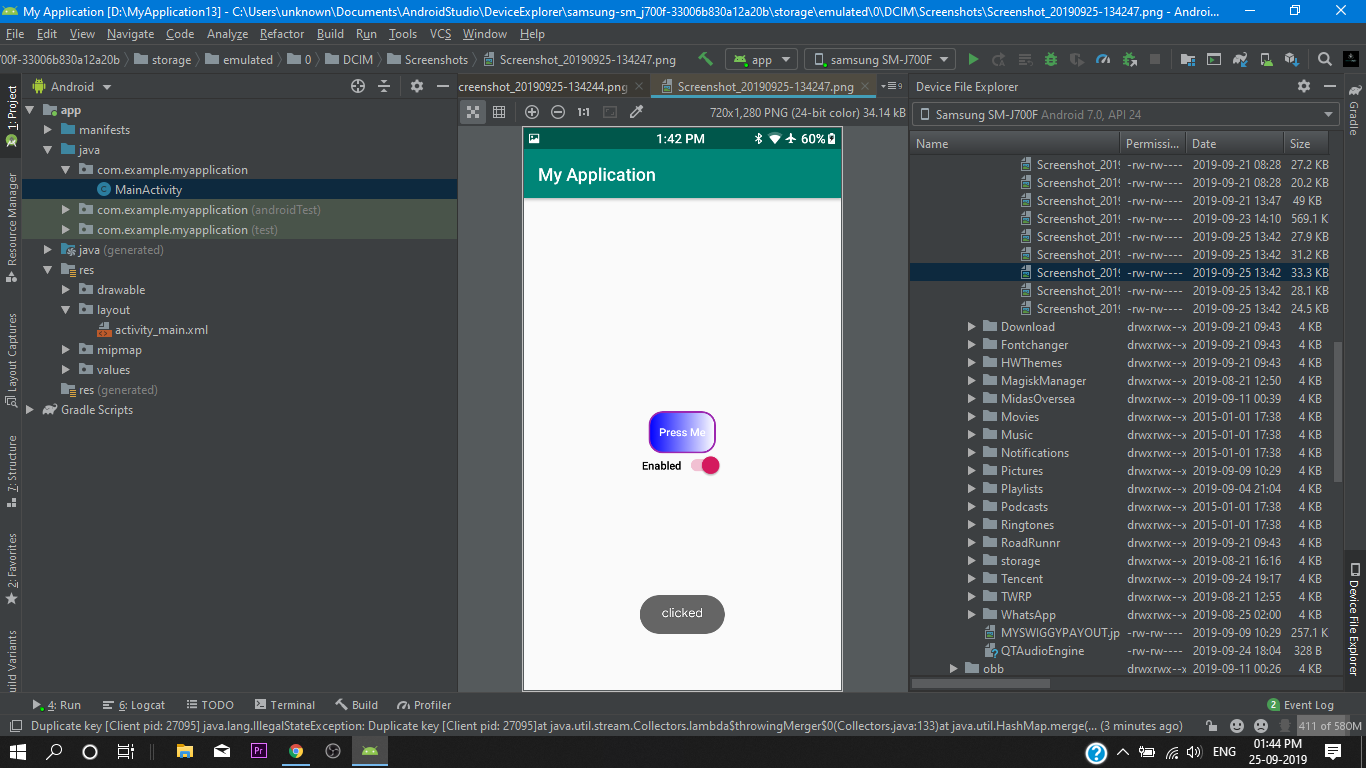
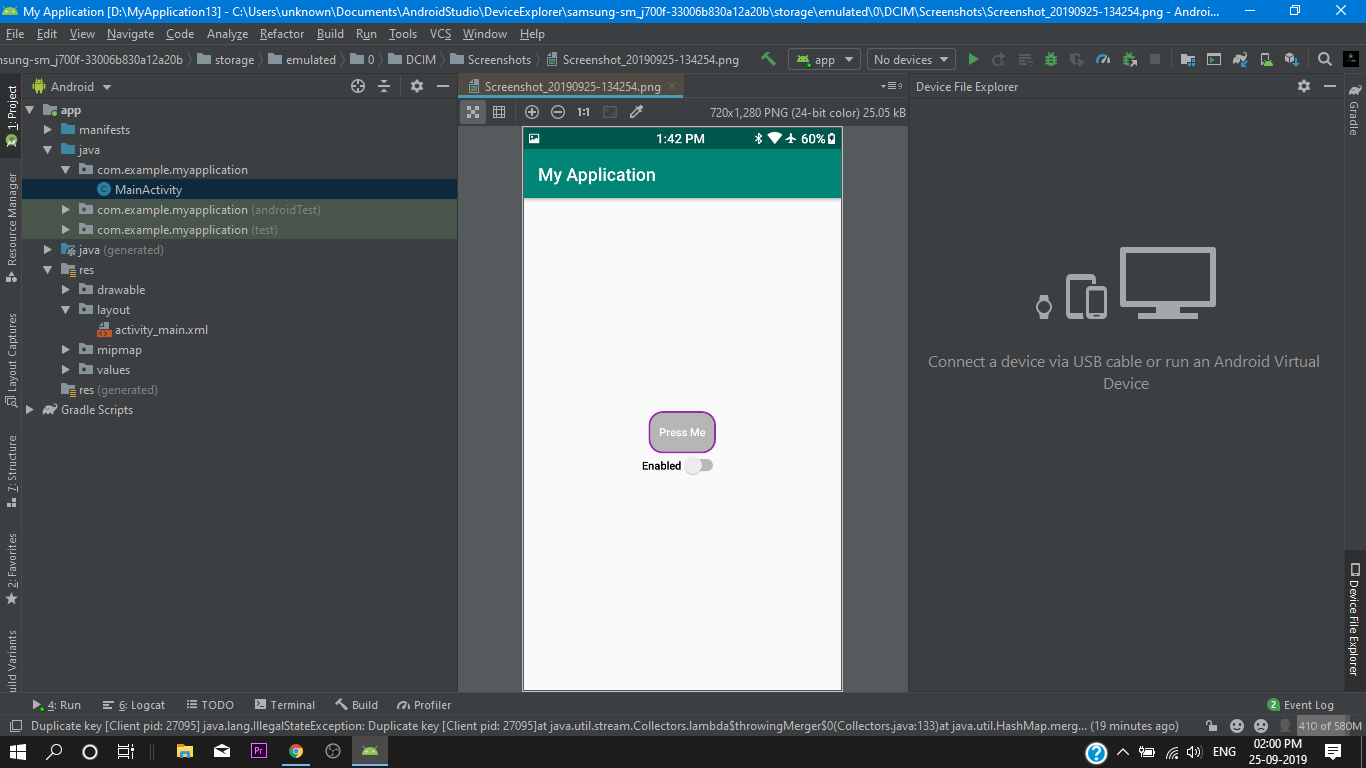
Finally we go into our Main Activity.xml and we add a button and set the background to our @drawable/custom_button and after doing this the system will take our three custom buttons as a one custom button and we will get our custom button background.
then we set a switch for disable purpose.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingBottom="8dp"
android:background="@drawable/custom_button"
android:text="Press Me" />
<Switch
android:id="@+id/btnSwitch"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checked="true"
android:text="Enabled"
/>
</LinearLayout>
after assigning the button and switch we go to our main activity.java file for give a behavior for our widgets.
Main Activity.JAVA
package com.example.myapplication;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.Switch;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final Button customButton = findViewById(R.id.btn);
Switch switchButton= findViewById(R.id.btnSwitch);
customButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"clicked", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
switchButton.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton ButtonView, boolean isChecked) {
if (isChecked) {
customButton.setEnabled(true);
} else {
customButton.setEnabled(false);
}
}
});
}
}
We have successfully created our shape drawable button. So Let’s Test it out!
So That’s all for today cod3’rs i hope now you got a understanding of shape drawable and you can also use this method in your projects to create a awesome looking custom button.
if you like this tutorial then make sure stay tuned for future upcoming tutorial’s